
Lithium batteries have become the preferred power source for many electric applications over the last few years and there is good reason for that. Items such as cell phones, medical devices (implanted pacemakers) and most recently electric cars rely on a battery that offers substantial run time and overall performance compared to previous designs found in alkaline (non-rechargeable) and lead acid (rechargeable) batteries.
Like most new technologies…it comes at a cost although that will inevitably change over time as adoption rates and standardization to lithium ion batteries become more mainstream.
How do lithium batteries perform?
Today’s lithium batteries have a myriad of applications and continues to grow annually as the demands from electronics and more recently the automotive industry expand their offerings.
A lithium battery offers up to 5,000 charging cycles or 10 years of service life and they can be discharged beyond 80% of the total capacity and still function following a proper recharge. Although these batteries are rated to sustain up to 5,000 charging cycles it’s important to note that translates to 100% output thru that timespan. Another significant advantage of a lithium battery is the fact that it delivers full voltage across the entire span of discharge. So if you have a a 12V lithium battery that has a discharge of approximately 50% you can still expect to get the full 12 volts, which is not the case with lead acid batteries.
How do lead acid batteries perform?
The lead acid battery is the most common type of battery found in cars and trucks that provide CCA (cranking amps) to start the engine and continuous power for accessories such as infotainment systems and lights. These batteries require virtually no maintenance other than charging, which made them ideal for automotive applications. Keep in mind today’s cars and trucks are equipped with an alternator that generates and provides power back to the battery to restore the amps lost while starting the engine and powers the onboard electric accessories.
Consider the performance of sealed lead acid (SLA) batteries that offer up to 500 charging cycles or 3-5 years of service life. A typical charge and use cycle of a rechargeable lead acid battery is 8 hours of use followed by 8 hours of charging followed by a cool down period due to the tremendous heat that is generated during charging. It must be pointed out that lead acid batteries are very finicky when it comes to charging and if the proper voltage and time is not applied the battery capacity will be significantly and permanently compromised. Contrary to a lithium battery, once a lead acid battery is depleted below 50% of its total capacity the battery is generally useless and in need of replacement.
The chart below provides a visual reference as to how the various states of discharge affect batteries relative to the capacity rating. As I mentioned above, the lithium ion (LiFeP04) battery delivers a constant capacity across the entire span of discharge.
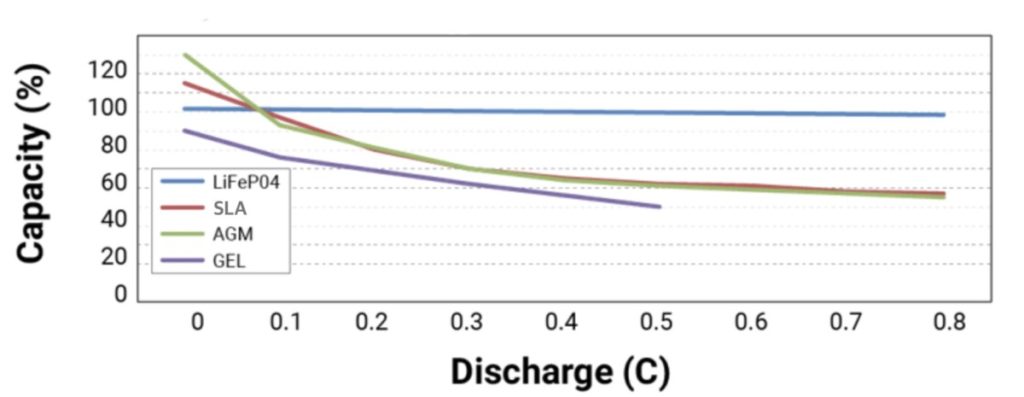
Today’s vehicles, boats and powersports toys are advanced to the point they require loads of battery power to operate the various onboard computers and infotainment systems. This is important to note because the typical lead acid battery was designed 100 years ago and although it has innovated over the years it was never intended to meet the demands of today’s designs. In fact, only 30% of lead acid batteries will reach their intended lifespan of 48 months.
A reported case study conducted by the manufacturer of Energizer batteries compared the performance of their AA Ultimate Lithium battery vs. the Max Alkaline battery revealing 8 and in some cases 10 more cycles from the lithium battery.
I would add to the consideration a feature that as an owner of a fishing boat and other powersports toys that rely on batteries are the self discharge rates. A lead acid battery will self discharge an average of 33% per month; whereas, a lithium battery will self discharge 2-3% per month. For users who don’t have consistent access to electricity where they store their toys for extended periods of time or don’t want to leave batteries on a charge this is a game changer.
How do lead acid batteries compare to lithium batteries?
I personally think a practical assessment of lithium vs. lead acid in a real world application involves the golf cart industry. Golf carts have operated on lead acid batteries for decades and have tremendous history with that application. It’s worth noting golf carts have reasonable demands put on them with daily use at golf courses across the country and a variation of terrain to include on and off pavement operation as well as hill climbs and descents.
Additional facts to consider are charge times and charge cycles when comparing lithium to lead acid (AGM) golf cart batteries:
| Performance Categories | Lead Acid | Lithium |
| Charge Time: | 8 hours | 3 hours |
| Charge Cycles: | 500 to 2,000 | 2,000 to 5,000 |
In the chart above it starts to become clear if you are running a golf course what the preferred battery technology is for your fleet of golf carts. Having the ability to turnover golf carts during a single day vs. having to maintain a larger fleet is likely a significant upfront cost savings.
How much do lithium batteries cost?
We have not touched on the cost, so let’s consider a lead acid vs. a lithium battery set up in a 48V configuration. The lead acid battery pack, which includes four 12V batteries (150Ah) will ring up at a cost between $1,150 to $1,300. Whereas a 48V lithium battery pack will run between $2,400 and $5,000 depending on use of 50Ah or 100Ah set ups.
Given the performance of the lithium vs. lead acid as it relates to charge cycles you would get 4 to 5 times the battery pack lifespan for twice to four times the cost. The cost becomes a net neutral event, but we must consider the simplicity in maintaining the lithium battery vs. lead acid. Lithium batteries can be charged at any capacity level; whereas, lead acid batteries will loose significant lifespan if partially charged batteries are regularly charged vs. a depleted battery. Unless all the lead acid carts are maintained in such a way to maximize performance then the lithium set up wins hands down.
It’s also worth noting, at least in the world of golf cart performance, a lithium battery configuration reduces the total weight of the battery pack resulting in a significant increase of the power to weight ratio. This results in less draw on the battery pack to operate the golf cart at maximum performance for the duration of golf rounds or other applications in which they are frequently used. As a general rule a lithium battery weighs roughly 50% less than an equivalent lead acid (AGM) battery.
Consider this thought as well, I stated early in this post lithium batteries provide continuous output at all levels of charge/discharge. You are probably thinking why would this matter. Well, a lead acid battery starts to loose output as the battery power is consumed and those of you that might be golfers have likely experienced this. At the beginning of the day golf carts have plenty of pep during acceleration and climbing hills; conversely, at the end of the day the golf cart seems sluggish and almost unwilling to tackle steep terrain.
Summary
To sum up the original question asking if lithium batteries are worth the cost….I would say yes and I believe the evidence will continue to mount in favor of this technology. The reduction in weight along with the increased lifespan are probably the two most important features that have come from the innovation of lithium technology. Be sure to look for firsthand reviews of lithium batteries in future post.
